Securing the Web: The Evolution of HTTPS/SSL Protocols
In the dynamic realm of cyberspace, the robustness of web security stands as a paramount concern. As we navigate through the intricate tapestry of online interactions, the evolution of HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) and its underlying SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) protocols emerges as a crucial narrative. This introduction serves as a gateway to unravel the historical trajectory and contemporary significance of these protocols, which play a pivotal role in fortifying the integrity, confidentiality, and authenticity of data exchanged over the World Wide Web. The journey encompasses the technological metamorphosis from early SSL iterations to the current TLS (Transport Layer Security) standards, shedding light on the constant battle between security measures and evolving cyber threats. By delving into the intricate nuances of HTTPS/SSL, we embark on a quest to understand the ever-changing landscape of web security and the relentless pursuit of a safer digital frontier.
Guardians of Online Security: Google’s Motivation Behind HTTPS/SSL
Google’s fervent advocacy for HTTPS/SSL protocols stems from a profound commitment to fortifying the fabric of online security. The motivation behind Google’s drive to champion these protocols lies in a steadfast dedication to creating a safer and more secure digital environment for users worldwide. Recognizing the escalating cyber threats and the imperative to safeguard sensitive user data, Google embarked on a mission to push for the widespread adoption of HTTPS, marking websites with a secure padlock in the address bar and labeling HTTP sites as “Not Secure.” This strategic move reflects a visionary approach to inspire a collective shift towards stronger encryption standards, reducing the vulnerability of user information to malicious actors. Google’s commitment to being the guardians of online security underscores the company’s pivotal role in shaping the digital landscape and fostering a culture of trust and reliability across the vast expanse of the internet.
Fortifying the Digital Ramparts: The Special Features of HTTPS/SSL
What sets HTTPS/SSL apart and renders it indispensable in fortifying the digital ramparts lies in its array of special features that collectively redefine the landscape of online security. At the core of its prowess is the encryption mechanism, a robust shield that cloaks transmitted data in an impervious layer, safeguarding it from prying eyes and potential cyber threats. This cryptographic safeguard not only ensures the confidentiality of user information but also guarantees the integrity of data during transit. Another hallmark feature is the establishment of a secure communication channel, where SSL/TLS protocols authenticate the identity of the website, mitigating the risk of phishing attacks and unauthorized intrusions. Moreover, the conspicuous visual cues, such as the padlock icon and the “https://” prefix, serve as trust indicators, fostering confidence among users by signaling a secure connection. In amalgamation, these distinctive features of HTTPS/SSL not only shield sensitive information but also cultivate a digital environment built on the pillars of trust, reliability, and uncompromising security.
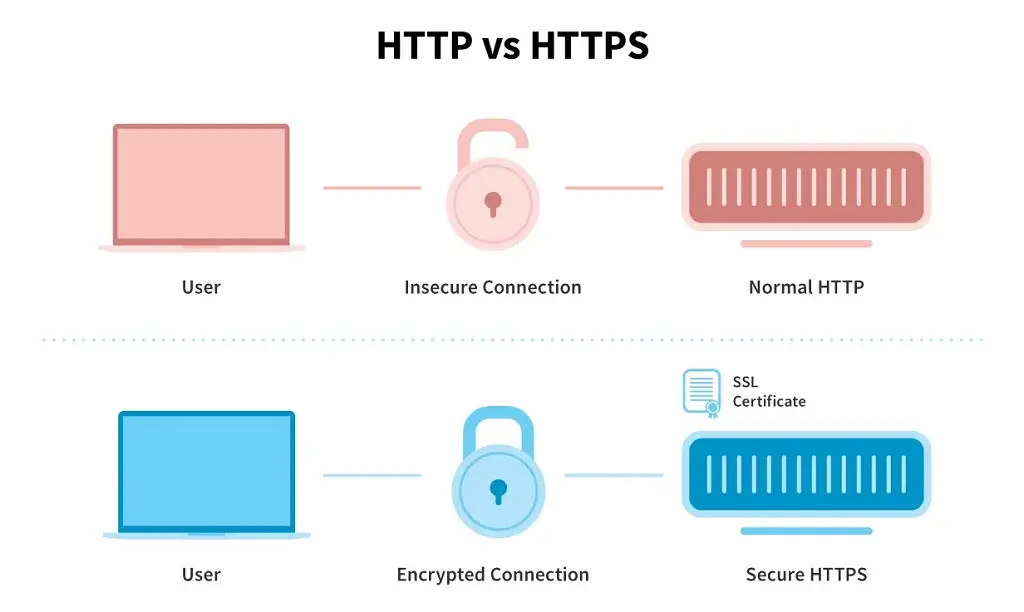
Cryptography Unveiled: Decrypting the Mechanisms of HTTPS/SSL
- Handshake Protocol:
-
-
- HTTPS/SSL initiates a secure connection through a handshake protocol where the client and server exchange information to establish a secure channel.
- This process involves the server presenting its digital certificate, which includes a public key.
-
- Public Key Cryptography:
-
-
- Public key cryptography forms the foundation, utilizing asymmetric encryption where each party possesses a public key and a private key.
- The server’s public key encrypts data that only the corresponding private key can decrypt, ensuring secure communication.
-
- Symmetric Encryption:
-
-
- Once the secure channel is established, HTTPS switches to symmetric encryption for the actual data transmission.
- A unique session key is generated for the duration of the connection, enhancing efficiency and security.
-
- Data Integrity through Hash Functions:
-
-
- Hash functions play a crucial role in ensuring data integrity during transmission.
- The server generates a hash of the data, and the client verifies this hash upon receiving the data to confirm its integrity.
-
- Certificate Authorities (CAs):
-
-
- Digital certificates issued by Certificate Authorities validate the authenticity of the server’s public key.
- Browsers come pre-installed with a list of trusted CAs, enhancing trust in the identity of the server.
-
- SSL/TLS Protocols:
-
-
- HTTPS relies on SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or its successor, TLS (Transport Layer Security), to establish and maintain secure connections.
- These protocols undergo continuous development to address vulnerabilities and adapt to evolving security standards.
-
- Padlock and HTTPS Prefix:
-
-
- Visual indicators like the padlock icon and the “https://” prefix in the URL bar signify a secure connection, instilling confidence in users.
-
- Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS):
-
-
- HTTPS often employs Perfect Forward Secrecy, which ensures that even if a long-term private key is compromised, past communications remain secure.
-
- Browser Warnings:
-
-
- Browsers may display warnings for websites without valid SSL certificates or those using outdated encryption protocols, encouraging a move towards stronger security measures.
-
- Continuous Evolution:
-
- The HTTPS/SSL ecosystem evolves to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities, emphasizing the importance of keeping encryption standards up to date for robust online security.
Browsing with Confidence: The User Experience in the HTTPS/SSL Era
- Enhanced Security: Users experience heightened security while browsing, as HTTPS/SSL encrypts data during transmission, safeguarding sensitive information from interception by malicious entities.
- Data Privacy Assurance: HTTPS ensures the privacy of user data by preventing unauthorized access, fostering confidence that personal information, login credentials, and financial details are kept confidential.
- Protection Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Users are shielded from man-in-the-middle attacks as SSL/TLS protocols verify the identity of the server, reducing the risk of data tampering or interception during communication.
- Trust Indicators: Visual cues like the padlock icon and the “https://” prefix in the URL bar serve as trust indicators, reassuring users that the website employs secure encryption protocols.
- Secure Online Transactions: E-commerce transactions, login processes, and other sensitive operations conducted over HTTPS inspire confidence, as users can trust that their financial and personal details are transmitted securely.
- Phishing Mitigation: HTTPS mitigates the risk of phishing attacks by ensuring that users interact only with legitimate websites. The visible indicators help users distinguish between secure and potentially malicious sites.
- Browser Warnings: Users benefit from browser warnings that alert them to potential security risks on websites lacking valid SSL certificates, prompting informed decisions about the safety of their online interactions.
- Improved SEO Ranking: Websites employing HTTPS receive a boost in search engine rankings, contributing to a positive user experience by ensuring that users are directed to secure and trustworthy websites.
- Cross-Browser Consistency: Users experience a consistent level of security across different browsers, as major browsers uniformly recognize and support HTTPS, creating a standardized and reliable online security environment.
- Encouraging Secure Practices: The ubiquity of HTTPS encourages website owners to prioritize security, fostering a culture of best practices in data protection and contributing to an overall safer online ecosystem.
Securing Digital Real Estate: HTTPS/SSL’s Impact on Website Credibility
- Credibility Enhancement: Implementation of HTTPS/SSL enhances the credibility of a website by signaling to users that the operator is committed to securing their data and ensuring a safe browsing experience.
- Trust Building: Trust is a crucial factor in online interactions, and the use of HTTPS builds trust among website visitors, assuring them that their information is transmitted securely.
- Search Engine Ranking Boost: Search engines prioritize secure websites, and adopting HTTPS positively impacts search engine rankings. Website operators benefit from increased visibility and traffic as a result.
- Positive User Experience: HTTPS contributes to a positive user experience, reducing the likelihood of security warnings and fostering a sense of trust that encourages users to engage with the website.
- Protection Against Phishing: By using HTTPS, website operators help protect users from phishing attacks, as the secure connection verifies the authenticity of the site and mitigates the risk of users falling victim to fraudulent activities.
- Legal and Compliance Benefits: HTTPS adoption aligns with legal and regulatory requirements related to data protection and privacy, ensuring that website operators comply with industry standards and avoid potential legal issues.
- Mitigation of Security Risks: Implementing HTTPS/SSL protocols mitigates security risks, reducing the likelihood of data breaches, unauthorized access, and other cyber threats that could tarnish the reputation of the website and its operator.
- Encouraging Secure Practices: The widespread adoption of HTTPS encourages a culture of security among website operators, prompting them to implement best practices in data protection, further contributing to a secure online ecosystem.
- Improved Conversion Rates: Users are more likely to complete transactions and engage with a website when they see the secure padlock and HTTPS in the URL, leading to improved conversion rates for e-commerce and other online activities.
- Competitive Advantage: Websites with HTTPS enjoy a competitive advantage, as users increasingly prioritize secure online experiences. By adopting HTTPS, website operators stay ahead in the evolving digital landscape and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
SSL Signals: The SEO Impact of HTTPS Adoption
- Search Ranking Boost: HTTPS adoption is a significant signal for search engines, and secure websites often receive a boost in search rankings compared to their non-secure counterparts.
- Google’s Preference: Google, the dominant search engine, explicitly favors HTTPS-encrypted websites, considering it as a ranking factor. Websites with HTTPS are more likely to appear higher in search results.
- Algorithm Adjustments: Search engine algorithms continually evolve, and the emphasis on website security, as indicated by HTTPS adoption, has become increasingly prominent in these algorithmic considerations.
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) as a Ranking Factor: Google has confirmed that SSL is a lightweight ranking factor, and websites with HTTPS may experience improved visibility and traffic as a result of this positive ranking factor.
- Page Loading Speed: SSL/TLS protocols, integral to HTTPS, can contribute to a faster and more efficient website performance, which is another factor considered by search engines when determining rankings.
- Mobile-First Indexing: With the shift towards mobile-first indexing, Google places additional importance on mobile-friendly and secure websites. HTTPS adoption aligns with these mobile-centric considerations.
- Reduced Bounce Rates: Users are more likely to stay on a secure website, contributing to lower bounce rates. Search engines interpret lower bounce rates as a positive signal, potentially improving a site’s overall SEO performance.
- Crawl Budget Allocation: Secure websites may receive a more favorable allocation of crawl budget by search engine bots. This ensures that search engines efficiently index and rank content on secure sites.
- Future-Proofing SEO Strategy: Given the increasing emphasis on website security, adopting HTTPS is a strategic move to future-proof SEO efforts, aligning with the evolving priorities of search engines and user expectations.
- User Experience and SEO Synergy: HTTPS not only aligns with search engine preferences but also contributes to a positive user experience. Search engines prioritize user satisfaction, making HTTPS adoption a synergistic approach to both SEO and user engagement.
Migrating to the Secure Side: Strategies for Adopting HTTPS/SSL
- SSL Certificate Acquisition: Obtain a valid SSL certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). Choose the type of certificate based on the needs of your website, whether it’s a single domain, subdomain, or wildcard certificate.
- Choose the Right SSL/TLS Protocol: Select the appropriate version of the SSL/TLS protocol for your website. TLS is the successor to SSL, and it’s recommended to use the latest version for improved security.
- Update Internal Links: Ensure that all internal links within your website point to the HTTPS version. This includes updating navigation menus, image sources, and any hard-coded links in your website’s code.
- Implement 301 Redirects: Set up 301 redirects from the HTTP version to the HTTPS version of your URLs. This ensures a seamless transition for both users and search engines and helps in preserving SEO rankings.
- Update Content Delivery Networks (CDN): If you use a CDN, make sure it is configured to support HTTPS. Update CDN settings and configurations to ensure a secure content delivery process.
- Update Third-Party Scripts and Resources: Review and update any third-party scripts, plugins, or resources used on your website to ensure compatibility with HTTPS. This includes social media widgets, analytics scripts, and advertising code.
- Update External Links and Social Media Profiles: Ensure that all external links pointing to your website use the HTTPS version. Update social media profiles and any online listings to reflect the secure URL.
- Update Robots.txt and XML Sitemap: Modify your website’s robots.txt file to include the HTTPS version of your sitemap. Update XML sitemaps to include HTTPS URLs to ensure search engines can crawl and index the secure content.
- Check and Update Rel Canonical Tags: Review rel canonical tags in your website’s HTML and ensure they point to the HTTPS version of your pages. This helps search engines understand the preferred version of your content.
- Test and Monitor: Conduct thorough testing after the migration to HTTPS to identify and resolve any issues. Use online tools to check for mixed content, and monitor website performance, ranking changes, and user feedback post-migration.
- Update Google Search Console Settings: If applicable, update your website’s settings in Google Search Console to reflect the HTTPS version. This includes submitting the new sitemap and updating the preferred domain setting.
- Communicate the Change: Inform your users, subscribers, and relevant stakeholders about the migration to HTTPS. Provide information on the enhanced security measures and assure them of a continued secure browsing experience.
Decrypting Myths: Clarifying Misconceptions About HTTPS/SSL
The adoption of HTTPS/SSL has become a cornerstone in enhancing online security, yet it is not immune to the perpetuation of myths and misconceptions. One prevalent myth suggests that implementing HTTPS is a cumbersome and intricate process, deterring website operators from securing their platforms. In reality, with advancements in technology and the availability of user-friendly tools, the migration to HTTPS has become more straightforward than ever. Another misconception revolves around the belief that HTTPS is only essential for e-commerce websites dealing with sensitive transactions. However, the broader truth is that HTTPS is a fundamental layer of security that benefits all websites, fostering user trust, and positively impacting search engine rankings. Dispelling these myths is essential to promoting a universal understanding of the accessibility and advantages that HTTPS/SSL afford, encouraging website operators to embrace these protocols for a safer and more secure online landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, debunking the myths surrounding HTTPS/SSL is paramount to fostering a collective understanding of the true nature and benefits of these security protocols. Contrary to misconceptions about complexity, the process of adopting HTTPS has evolved to be more user-friendly and accessible, making it an achievable endeavor for website operators. Dismissing the notion that HTTPS is solely pertinent to e-commerce platforms is equally vital, as its universal application enhances trust, credibility, and search engine rankings across all websites. By decrypting these myths, we unveil the reality that HTTPS/SSL is not merely a technological accessory but a foundational element that fortifies the digital realm, ensuring a secure and resilient online environment for users and website operators alike. Embracing HTTPS becomes not just a security measure but a commitment to building a safer and more trustworthy internet landscape.




